-
-
- Created by John Burk, last modified on Feb 01, 2017
Step by step instructions for submitting XSI jobs with Qube!
Install Jobtypes
In order to submit directly from XSI, you will need to install the XSI jobtype.
Installation:
If you are not familiar with the installation process please see Installing Qube!
You will need to select "XSI Jobtype" during the installation process
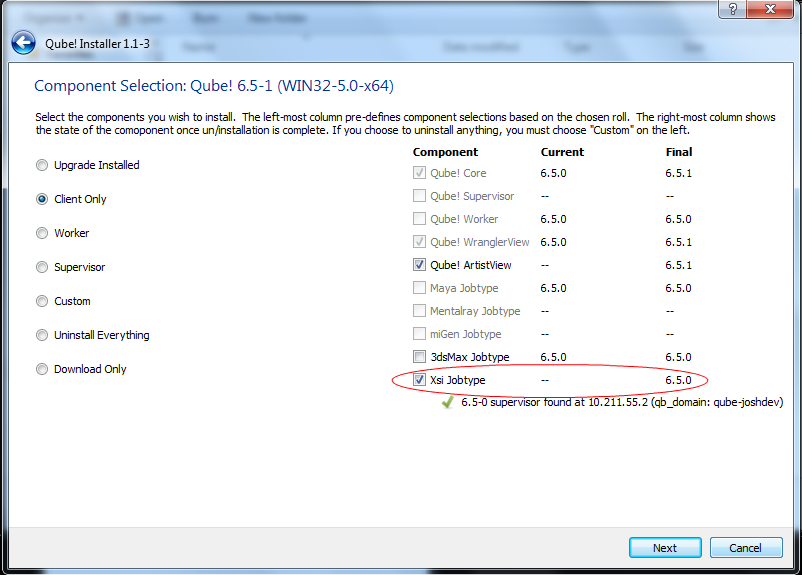
Alternatively:
If you only wish to use the "Batch XSI jobs" you can install the InApp plugins via the Qube! WranglerView.
File > Install App UI > Install XSI BatchRender App UI
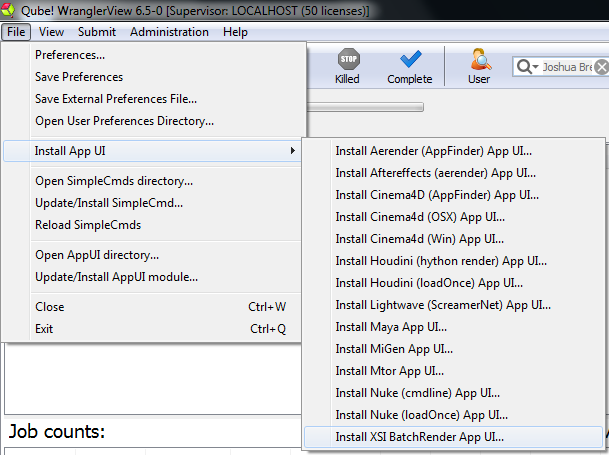
Once installed you should be able to locate the "Qube!" menu in XSI. With a scene loaded in XSI choose "Submit Render Job..." or "Submit Batch Render..." depending on your requirements.
Render vs Batch Render
IconWhat's the difference?
Submit Render will open a copy (instance) of XSI on the Worker that picks up the job, and that instance will render frames as assigned by the Supervisor. Since the scene file is only being opened one time, this can be faster to generate the full sequence.
Submit Batch Render will use the command line to open a new instance of the XSI file for each frame that it renders. Although this can be slower for large scenes, it can also be more flexible in large, complex environments.
This will present a pre-filled submission UI like the one shown here. Ensure sections marked in red have the correct details.
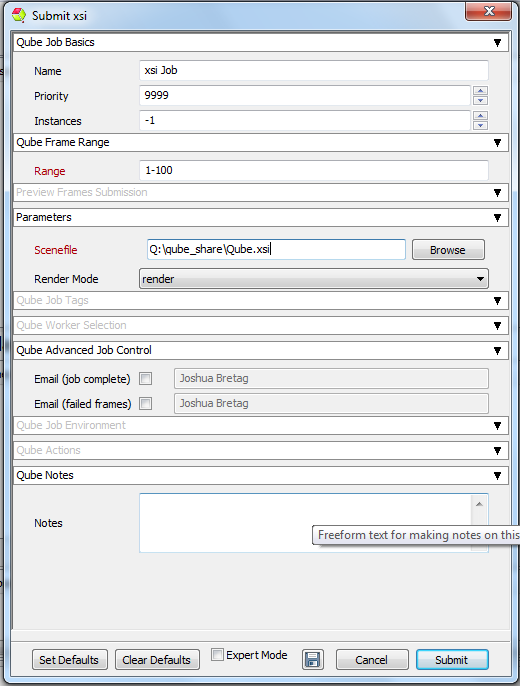
Click 'Submit'
For further details on the submission UI see below.
Job Submission Details
Not all sections need to be filled in in order to render only the fields marked in red are required.

Name
This is the name of the job of the job so it can be easily identified in the Qube! UI.
Priority
Every job in Qube is assigned a numeric priority. Priority 1 is higher than priority 100. This is similar to 1st place, 2nd place, 3rd place, etc. The default priority assigned to a job is 9999.
Instances
This is the number of copies of the application that will run at the same time across the network. The combination of "Instances=1" and "Max Instances=-1" means that this job will take as much of the farm as it can, and all jobs will share evenly across the farm.
Examples:
On a 12 slot(core) machine running Maya if you set
"Instances" to 4
"Reservations" to "host.processors=3"
Qube! will open 4 sessions of Maya on the Worker(s) simultaneously, which may consume all slots/cores on a given Worker.
if you set
"Instances" to 1
"Reservations" to "host.processors=1+"
Qube will open 1 session of Maya on a Worker, consuming all slots/cores ("host.processors=1+" is used for all slots/cores).
Max Instances
If resources are available, Qube! will spawn more than 'Instances' copies of the application, but no more than 'Max Instances'. The default of -1 means there is no maximum. If this is set to 0, then it won't spawn more than 'Instances' copies.
More on Instances & Reservations & SmartShare Studio Defaults
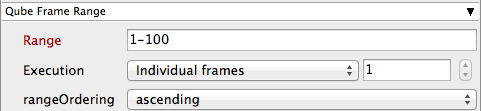
Range
Frame range for the job (e.g 1-100, or 1-100x3, or 1,3,7,10)
Most jobs require a frame range to execute on the workers. You can set this range in a few different ways :
- "1-100" will just render the range between 1 and 100
- "1-100x3" will render the range 1 to 100, every third frame, so 1, 4, 7, etc.
- "1,3,7,10" will only render the selected frames 1,3,7,10
Execution
How to break up frame range to be executed. Use QB_START_FRAME, QB_END_FRAME and QB_FRAME_NUMBER
When submitting a job to the farm it may be more efficient to "chunk" your job. This means that when the job is sent to the worker it tells the worker to render N consecutive frames before requesting more work. You would do this to keep from reopening the scene file for each frame. Large scene files can take substantial time to open, which is wasteful across dozens or hundreds of frames.
The drop down options are below:
- "Individual frames" this tells the worker to render 1 frame at a time.
- "Chunks with n frames" this tells the worker to render consecutively the number of frames specified in the field.
- "Split into n partitions" this tells the worker to render consecutively the total frames in the range divided by the number in the field.
Examples:
- range 1-100 with "individual frames" set will render 1 frame at a time
- range 1-100 with "Chunks with n frames" and the field set to 5 will send 20 frames to each instance
- range 1-100 with "Split into n partitions" and the field set to 4 will send 25 frames to each instance
rangeOrdering
Order to render the items. (Ascending=1,2,3,4,5...,Descending=10,9,8...,Binary=first,middle,last...)
You can set the order in which your frames are rendered. The drop down options are:
- "Ascending" - this will render the frames counting upwards from your start frame
- "Decending" - this will render the frames counting backwards from your end frame
- "Binary" - This will render the first, last, and middle frames of the range, then the middle frame of the first half and the middle frame of the second half, and so on. This is useful for sampling the frames in the sequence to make sure it is rendering correctly.
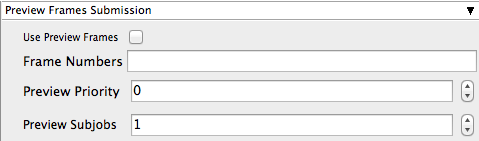
Use Preview Frames
Enabling preview frames will create 2 jobs:
- A primary dependent job with a higher priority that will render the selected frames first
- A secondary job with lower priority that will render the remaining frames. This will return the selected frames faster so that you can check the accuracy of your renders.
Frame Numbers
Choose the frames that you wish to render first. If left blank the default is to render the first frame, the last frame and the middle frame in that order. You can select specific frames by adding comma separated frame numbers e.g 1,2,10,15,75, or a range with, e.g., 1-100x5 (1 to 100, every 5th frame)
Preview Priority
Choose the priority for the preview job. This can be set by the site admin.
Preview Subjobs
Choose the number of instances / subjobs for the preview frames. By default, this is equal to the number of preview frames - that is, it will try to do all the preview frames at the same time.
Note that when you submit a job with preview frames enabled, it will actually submit 2 jobs—one with the preview frames list at a higher priority, and another with the rest of the agenda, at the normal priority (as specified in the job's Priority field). You will get, consequently, 2 job IDs for the submission.
XSI Specific Parameters
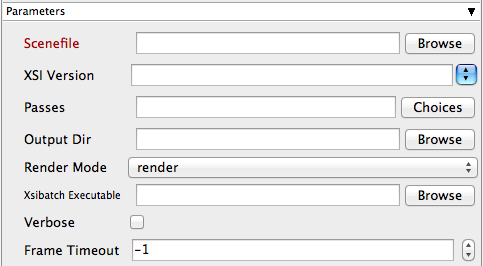
Scenefile
The path to the XSI scene file. This is a required field for submission. Make sure the path is accessible by the Workers.
XSI Version
Select or manually enter the Softimage/XSI version to be used on the Workers.
Passes
Choose or list the comma-separated passes to render. These are named in your XSI scene.
Output Dir
The output directory for images. Make sure this location is accessible by the Workers.
Render Mode
Override the scene file's render mode. The default is "render".
Xsibatch Executable
The explicit path to xsibatch executable (optional) on the Workers. Be aware that if you are submitting from one OS to a different one, the path will be different for the Workers.
Verbose
Choose the level of detail you would like the logs to provide.
Frame Timeout
Kill subjobs if a frame runs longer than this value (in seconds).
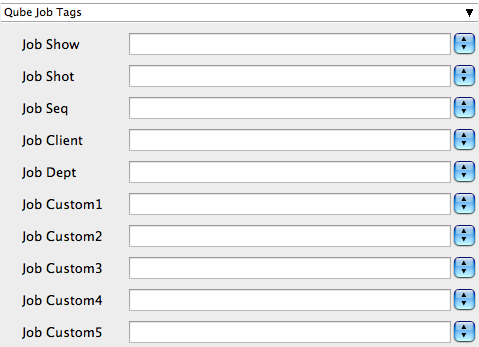
Qube Job Tags
New in Qube 6.5
Note: The Job Tags section of the submission UI will not be visible unless they are turned on in the Preferences in the Wrangler View UI. Job Tags are explained in detail on the Job Tags page.
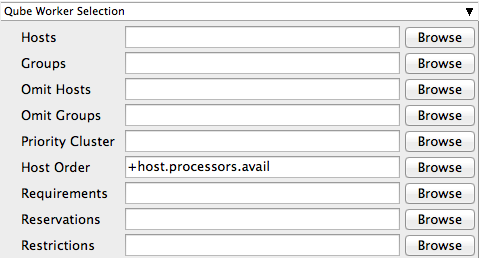
Hosts
Explicit list of Worker hostnames that will be allowed to run the job (comma-separated).
Groups
Explicit list of Worker groups that will be allowed to run the job (comma-separated). Groups identify machines through some attribute they have, eg, a GPU, an amount of memory, a license to run a particular application, etc. Jobs cannot migrate from one group to another. See worker_groups.
Omit Hosts
Explicit list of Worker hostnames that are not allowed run the job (comma-separated).
Omit Groups
Explicit list of Worker groups that are not allowed to run the job (comma-separated).
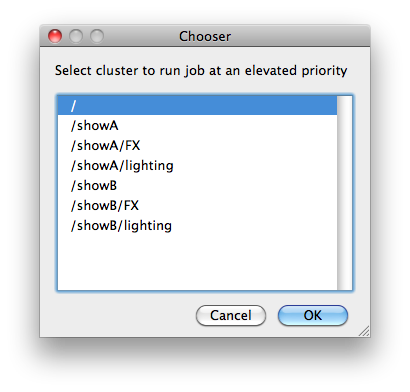
Priority Cluster
Clusters are non-overlapping sets of machines. Your job will run at the given priority in the given cluster. If that cluster is full, the job can run in a different cluster, but at lower priority. Clustering
 |
|---|
Example:
|
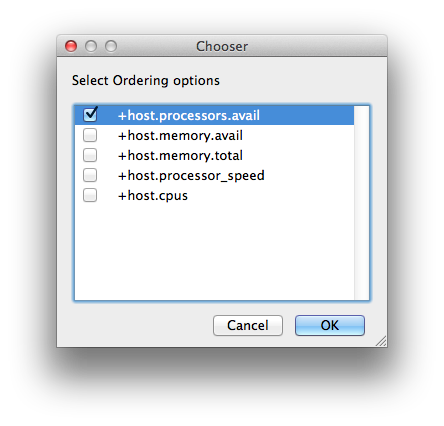
Host Order
Order to select Workers for running the job (comma-separated) [+ means ascending, - means descending].
 |
|---|
Host Order is a way of telling the job how to select/order workers
|
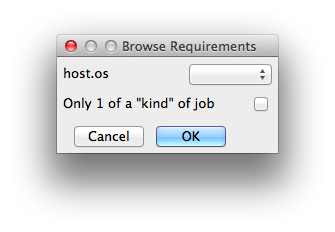
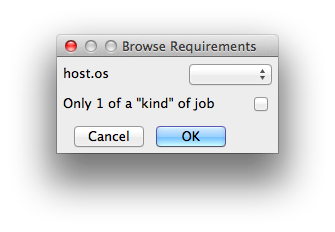
Requirements
Worker properties needed to be met for job to run on that Worker (comma-separated, expression-based). Click 'Browse' to choose from a list of Host Order Options.
 |
|---|
Requirements is a way to tell the workers that this job needs specific properties to be present in order to run. The drop-down menu allows a choice of OS:
You can also add any other Worker properties via plain text. Some examples:
With integer values, you can use any numerical relationships, e.g. =, <, >, <=, >=. This won't work for string values or floating point values. Multiple requirements can also be combined with AND and OR (the symbols && and || will also work). The 'Only 1 of a "kind" of job' checkbox will restrict a Worker to running only one instance with a matching "kind" field (see below). The prime example is After Effects, which will only allow a single instance of AE on a machine. Using this checkbox and the "Kind" field, you can restrict a Worker to only one running copy of After Effects, while still leaving the Worker's other slots available for other "kinds" of jobs. |
Reservations
Worker resources to reserve when running job (comma-separated, expression-based).
 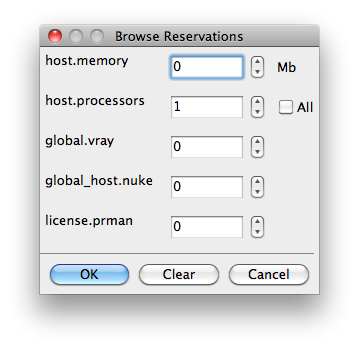 |
|---|
Reservations is a way to tell the workers that this job will reserve the specific resources for this job. Menu items:
Other options:
|
Restrictions
Restrict job to run only on specified clusters ("||"-separated) [+ means all below, * means at that level]. Click 'Browse' to choose from a list of Restrictions Options.
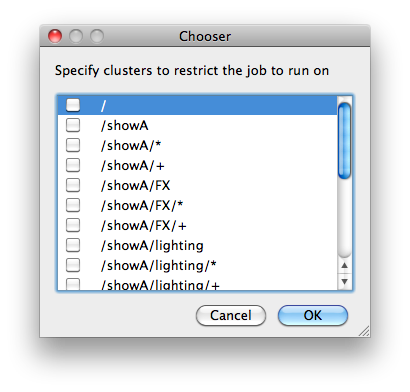 |
|---|
Restrictions is a way to tell the workers that this job can only run on specific clusters. You can choose more than one cluster in the list. Examples:
|
See Also
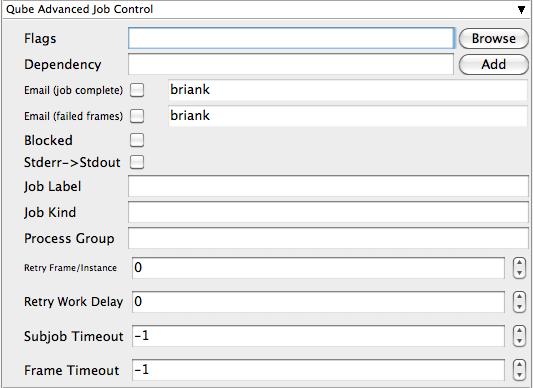
Flags
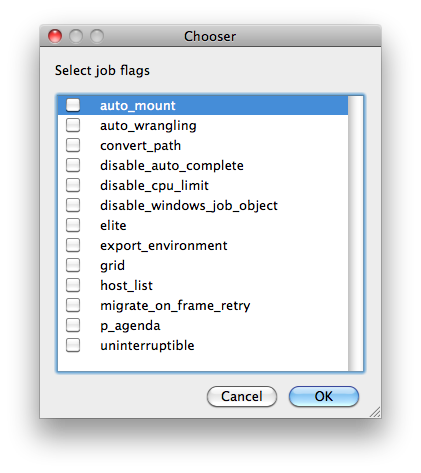
List of submission flag strings (comma separated). Click 'Browse' to choose required job flags.
|
|---|
| See this page for a full explanation of flag meanings |
Dependency
Wait for specified jobs to complete before starting this job (comma-separated). Click 'Add' to create dependent jobs.
 |
|---|
You can link jobs to each other in several ways:
The second menu chooses between "job" (the entire set of frames) and "work" (typically a frame). So to link frame 1 of one job to frame 1 of a second, job, you would choose "work" in this menu. If you want to wait for all the frames of one job to complete before starting a second, then choose "job". The other option, "subjob", refers to the instance of a job. This is much less common, but means that, for example, the instance of Maya that was running frames has completed. For a complete description on how to define complex dependencies between jobs or frames, please refer to the Callbacks section of the Developers Guide. |
Email (job complete)
Send email on job completion (success or failure). Sends mail to the designated user.
Email (failed frames)
Sends mail to the designated user if frames fail.
Blocked
Set initial state of job to "blocked".
Stderr->Stdout
Redirect and consolidate the job stderr stream to the stdout stream. Enable this if you would like to combine your logs into one stream.
Job Label
Optional label to identify the job. Must be unique within a Job Process Group. This is most useful for submitting sets of dependent jobs, where you don't know in advance the job IDs to depend on, but you do know the labels.
Job Kind
Arbitrary typing information that can be used to identify the job. It is commonly used to make sure only one of this "kind" of job runs on a worker at the same time by setting the job's requirements to include "not (job.kind in host.duty.kind)". See How to restrict a host to only one instance of a given kind of job, but still allow other jobs
Process Group
Job Process Group for logically organizing dependent jobs. Defaults to the jobid. Combination of "label" and "Process Group" must be unique for a job. See Process group labels
Retry Frame/Instance
Number of times to retry a failed frame/job instance. The default value of -1 means don't retry.
Retry Work Delay
Number of seconds between retries.
Subjob Timeout
Kill the subjob process if running for the specified time (in seconds). Value of -1 means disabled. Use this if the acceptable instance/subjob spawn time is known.
Frame Timeout
Kill the agenda/frame if running for the specified time (in seconds). Value of -1 means disabled. Use this if you know how long frames should take, so that you can automatically kill those running long.
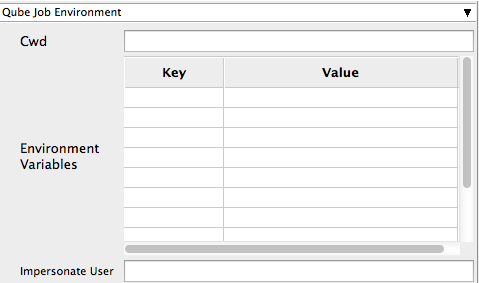
Cwd
Current Working Directory to use when running the job.
Environment Variables
Environment variables override when running a job. You can specify key/value pairs of environment variables
This is useful when you might need different settings for your render applications based on different departments or projects.
Impersonate User
You can specify which user you would like to submit the job as. The default is the current user. The format is simply <username>. This is useful for troubleshooting a job that may fail if sent from a specific user.
Example:
Setting "josh" would attempt to submit the job as the user "josh" regardless of your current user ID.
Note: In order to do this, the submitting user must have "impersonate user" permissions.
GenerateMovie
Select this option to create a secondary job that will wait for the render to complete then combine the output files into a movie.
Note: For this to work correctly the "Qube (ImagesToMovie) Job..." has to be setup to use your studios transcoding application.
Account
Arbitrary accounting or project data (user-specified). This can be used for creating tags for your job.
You can add entries by typing in the drop-down window or select already created accounts from the drop-down.
See also Qube! Job Tags
Notes
Freeform text for making notes on this job. Add text about the job for future reference. Viewable in the Qube UI.
- No labels
- Powered by Scroll Content Management Add-ons for Atlassian Confluence 5.6.6 | 2.8.10
- Powered by Scroll Content Management Add-ons for Atlassian Confluence.