-
-
- Created by John Burk, last modified on Feb 01, 2017
Step by step instructions for submitting Maxwell jobs with Qube!
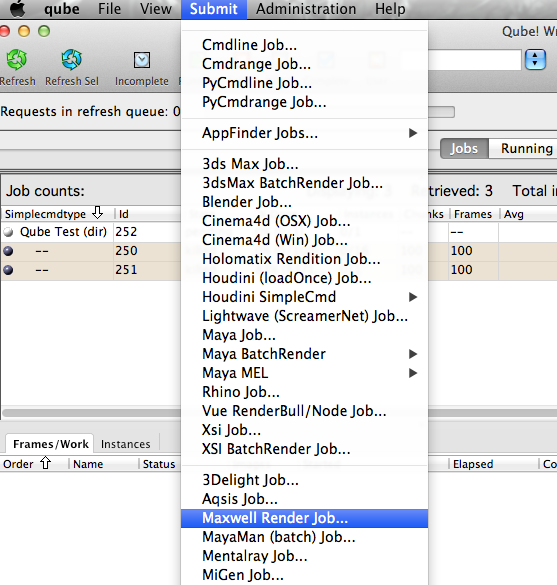
It is not currently possible to submit directly from Maxwell ("InApp" support), so you will submit from the Qube! WranglerView. Open the Submit menu and choose "Maxwell Render Job..." as shown here.
You will be presented with a Submission UI like this. Ensure sections marked in red have the correct details.
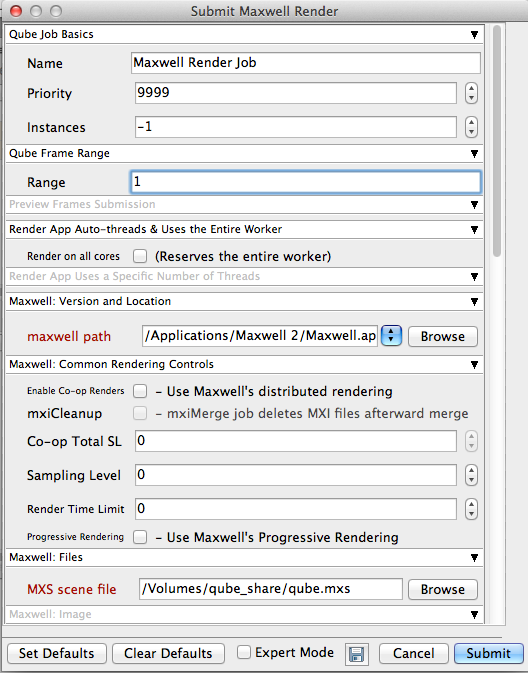
Click "Submit"
If you have selected the tick box "Enable Co-op Renders" you will be presented with a secondary window
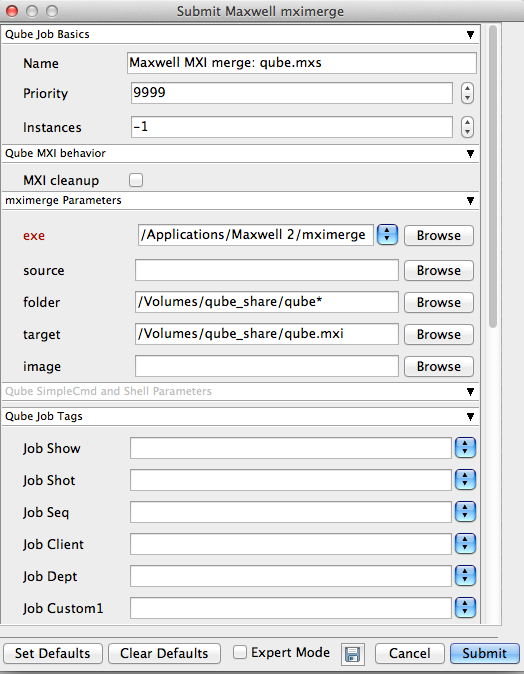
Click "Submit" again.
Job Submission Details
Not all sections need to be filled in in order to render only the fields marked in red are required

Name
This is the name of the job of the job so it can be easily identified in the Qube! UI.
Priority
Every job in Qube is assigned a numeric priority. Priority 1 is higher than priority 100. This is similar to 1st place, 2nd place, 3rd place, etc. The default priority assigned to a job is 9999.
Instances
This is the number of copies of the application that will run at the same time across the network. The combination of "Instances=1" and "Max Instances=-1" means that this job will take as much of the farm as it can, and all jobs will share evenly across the farm.
Examples:
On a 12 slot(core) machine running Maya if you set
"Instances" to 4
"Reservations" to "host.processors=3"
Qube! will open 4 sessions of Maya on the Worker(s) simultaneously, which may consume all slots/cores on a given Worker.
if you set
"Instances" to 1
"Reservations" to "host.processors=1+"
Qube will open 1 session of Maya on a Worker, consuming all slots/cores ("host.processors=1+" is used for all slots/cores).
Max Instances
If resources are available, Qube! will spawn more than 'Instances' copies of the application, but no more than 'Max Instances'. The default of -1 means there is no maximum. If this is set to 0, then it won't spawn more than 'Instances' copies.
More on Instances & Reservations & SmartShare Studio Defaults
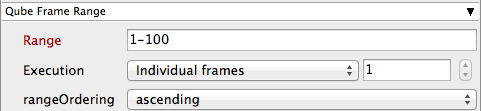
Range
Frame range for the job (e.g 1-100, or 1-100x3, or 1,3,7,10)
Most jobs require a frame range to execute on the workers. You can set this range in a few different ways :
- "1-100" will just render the range between 1 and 100
- "1-100x3" will render the range 1 to 100, every third frame, so 1, 4, 7, etc.
- "1,3,7,10" will only render the selected frames 1,3,7,10
Execution
How to break up frame range to be executed. Use QB_START_FRAME, QB_END_FRAME and QB_FRAME_NUMBER
When submitting a job to the farm it may be more efficient to "chunk" your job. This means that when the job is sent to the worker it tells the worker to render N consecutive frames before requesting more work. You would do this to keep from reopening the scene file for each frame. Large scene files can take substantial time to open, which is wasteful across dozens or hundreds of frames.
The drop down options are below:
- "Individual frames" this tells the worker to render 1 frame at a time.
- "Chunks with n frames" this tells the worker to render consecutively the number of frames specified in the field.
- "Split into n partitions" this tells the worker to render consecutively the total frames in the range divided by the number in the field.
Examples:
- range 1-100 with "individual frames" set will render 1 frame at a time
- range 1-100 with "Chunks with n frames" and the field set to 5 will send 20 frames to each instance
- range 1-100 with "Split into n partitions" and the field set to 4 will send 25 frames to each instance
rangeOrdering
Order to render the items. (Ascending=1,2,3,4,5...,Descending=10,9,8...,Binary=first,middle,last...)
You can set the order in which your frames are rendered. The drop down options are:
- "Ascending" - this will render the frames counting upwards from your start frame
- "Decending" - this will render the frames counting backwards from your end frame
- "Binary" - This will render the first, last, and middle frames of the range, then the middle frame of the first half and the middle frame of the second half, and so on. This is useful for sampling the frames in the sequence to make sure it is rendering correctly.
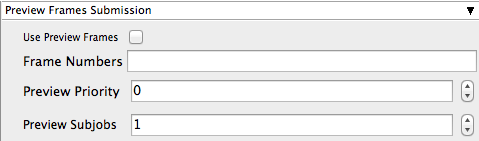
Use Preview Frames
Enabling preview frames will create 2 jobs:
- A primary dependent job with a higher priority that will render the selected frames first
- A secondary job with lower priority that will render the remaining frames. This will return the selected frames faster so that you can check the accuracy of your renders.
Frame Numbers
Choose the frames that you wish to render first. If left blank the default is to render the first frame, the last frame and the middle frame in that order. You can select specific frames by adding comma separated frame numbers e.g 1,2,10,15,75, or a range with, e.g., 1-100x5 (1 to 100, every 5th frame)
Preview Priority
Choose the priority for the preview job. This can be set by the site admin.
Preview Subjobs
Choose the number of instances / subjobs for the preview frames. By default, this is equal to the number of preview frames - that is, it will try to do all the preview frames at the same time.
Note that when you submit a job with preview frames enabled, it will actually submit 2 jobs—one with the preview frames list at a higher priority, and another with the rest of the agenda, at the normal priority (as specified in the job's Priority field). You will get, consequently, 2 job IDs for the submission.
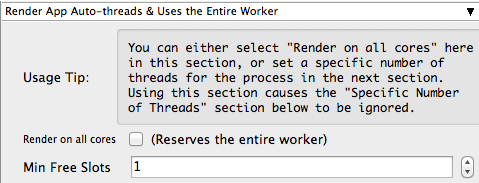
New in 6.4-4
For applications/renderers that do not support using all cores while rendering (or changing that behavior, eg AfterEffects or 3dsMax), this section is not visible.
Render on all Cores
Checking this box means that once this job is assigned to a machine, no more jobs or instances will be assigned to the same machine until this job is complete. You might choose this if your know your render job is very memory intensive and shouldn't run alongside other jobs.
Min Free Slots
This is the number of slots that must be available on a worker in order for the worker to accept the job. For example, if you choose '1', a worker with 7 out of 8 cores already in use will still accept this job. However, if you were to choose '2', the same machine under the same circumstances would not accept the job.
Preemption
IconThis option does not preempt any previously running instances on the worker, it only prevents additional instances from being assigned to this worker.

New in 6.4-4
For applications/renderers that do not support setting a specific number of threads, this section is not visible.
Slots = Threads
If this box is checked, it tells Qube and the application (eg, Maya) to use the specific number of threads listed in the "Specific Thread Count" field. If this is not checked, then the "Specific Thread Count" value is passed only to the application, but Qube is unaware of the number of cores/slots it should reserve. In most cases, you will want to check this box, unless you have Designer licenses, in which case you would only set the numeric value.
Specific Thread Count
This tells the renderer to use a specific number of threads for rendering. The default is one thread, which for any modern renderer will underperform, and when combined with the slots=threads, will swamp most workers by running as many instances as there are slots (eg, a 24 core machine would run 24 instances of the application/renderer). A better value is 8 (assuming you have 8 cores, as most modern machines do) which means that each instance of the job will use 8 threads to render, and, when combined with slots=threads, will reserve 8 slots while doing so.
Designer License
IconDesigner licenses are restricted to 1 slot, so if you are using a Qube Designer license, set the Specific Thread Count, but do not check the "Slots=Threads" option.
Maxwell Specific Parameters
maxwell path
The explicit path to Maxwell v2 executable on the Workers.
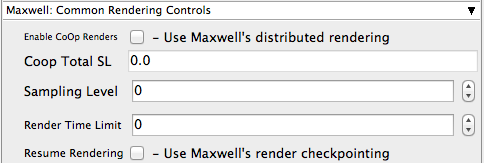
Enable CoOp Renders
Perform a cooperative render. Setting this to co-op will create a secondary MXIMerge job that combines the finished MXI's upon completion. Make sure you set the "Instances" parameter to more than 1, in the "Qube Job Basics" section above.
Coop Total SL
If CoOp rendering is selected above, this sets the sampling level for the final render, when the MXIs are all merged. Set to 0 to have all instances respect the value set in the "Sampling Level" box below.
Sampling Level
Override the render quality level set in the MXS.
Render Time Limit
Time (in minutes) that the renderer is allowed to run (per-frame), overrides the Time value saved in MXS.
Resume Rendering
Automatically resume the render if the MXI file exists.
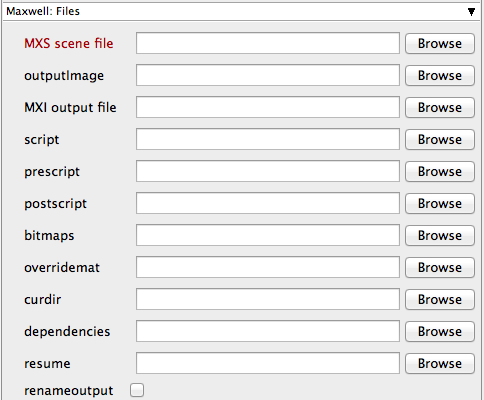
MXS scene file
The MXS scene to render. This is a required field for submission. Important: Make sure that the Workers have access to this file path.
outputImage
This will override the full path and name of the image file specified in the MXS scene. Important: Make sure that the Workers have access to this file path.
MXI output file
The MXI output file containing information about the rendering process. This allows for resuming a previously rendered image. If not specified, the MSI will use the same name and path as the MXS scene.
script
Names a script to load and run on the Worker(s).
prescript
Names a prescript to load and run on the Worker(s).
postscript
Names a postscript to load and run on the Worker(s).
bitmaps
Set an alternative folder path for the location of the bitmaps. If set to "0", it will discard all the bitmaps.
overridemat
Override all the materials in the scene using the materials found at the given path. Make sure that path is visible to all the Workers.
curdir
Set the current directory during the render. This is useful where relative paths are used to locate textures and other dependencies.
dependencies
Set an alternative folder path for the dependencies location.
resume
This resumes a previously rendered image and update the MXI file.
renameoutput
When this flag is used, Maxwell Render does not write the MXI file directly to the given output path; instead, it will write to a temporary file and then rename/move the result to the final path.
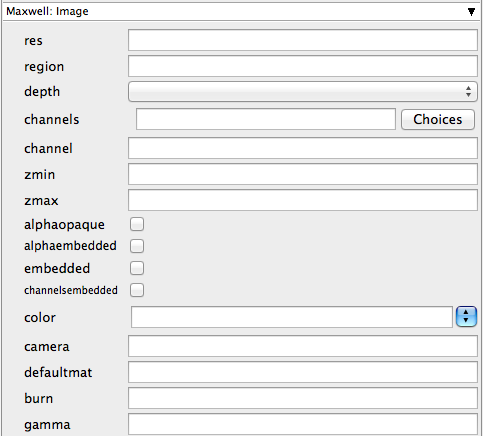
res
Overrides the scene resolution defined in the file. Format is WxH, e.g., 800x600
region
Describes a region type to render, along with its coordinates. The format is "type,x1,y,x2,y2" where "type" is one of "full", "region" or "blowup" and "x1,y1,x2,y2" are the coordinates of the rectangular region to render or enlarge.
depth
Overrides the image depth settings in the scene file.
channels
Overrides the channels that Maxwell will export, as defined in the scene file. Possible channels are r, a, ao, s, m, i, zmin, zmax.
channel
Overrides each exported channels export status and format. The format is [channel_name],[on|off],[depth(8,16,32)],[format]. All the parameters are optional except for the first one. Examples: channel:alpha,on,32,tif... channel:material... channel:object,off
zmin
Overrides the zmin values of the zbuffer channel.
zmax
Overrides the zmax values of the zbuffer channel.
alphaopaque
Enable opaque mode in the alpha channel.
alphaembedded
Enables embedded alpha.
embedded
Embeds the selected channel when the output format allows it.
channelsembedded
Enable/disable embedding all the channels as images layers if the format supports it.
color
Overrides the color space setting in the scene file.
camera
Specifies a camera to render. If not specified, will default to the active camera.
defaultmat
Overrides the path to the default materials.
burn
Overrides the burn value set in the scene file.
gamma
Overrides the gamma value set in the scene file.
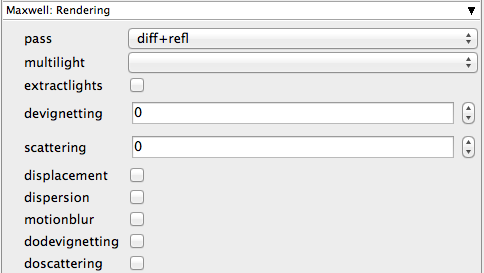
pass
Overrides the render pass that is set in the scene file.
multilight
Enables the multi-light function for storing an MSI file with separate information about the emitters.
extractlights
If this is enabled, each light will be saved in a separate file.
devignetting
Overrides the scene file's setting (or default) for the devignetting value.
scattering
Overrides the scene file's setting (or default) for the scattering value.
displacement
Enables the displacement calculations for the whole scene. Not necessary if not already set in the scene file.
dispersion
Enables the dispersion calculations for the whole scene. Not necessary if not already set in the scene file.
motionblur
Enables motion blur calculations for the whole scene. Not necessary if not already enabled in the scene file.
dodevignetting
Enables devignetting for the whole scene. Not necessary if not already enabled in the scene file.
doscattering
Enables lens scattering. Not necessary if not already enabled in the scene file.
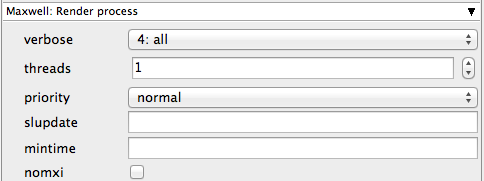
verbose
Verbosity level. Choose the level of detail you would like the logs to provide.
threads
The number of threads to render with (0 means use the maximum available).
priority
The Maxwell Renderer process priority.
slupdate
The number of seconds between sampling refreshes. If not set, the engine will choose an interval automatically.
mintime
Set the time to impose a minimum time for saving MXI files to disk. This is the equivalent of the preference "Min.Time"
nomxi
Force Maxwell Render to save only the output image, and not the MXI file.
Internal(Range)
Sequence of frames to render, overriding the scene settings. The format is comma-separated frames and frame ranges. For example, 12,21-30,99-102 would render frame 12, frames 21-30, and frames 99-102.
Cmd Template
This is used to create the command string for launching the job on the worker. It will be set differently depending on the application you are launching from.
Shell (Linux/OSX)
Explicitly specify the Linux/OS X shell to use when executing the command (defaults to /bin/sh).
Qube Job Tags
New in Qube 6.5
Note: The Job Tags section of the submission UI will not be visible unless they are turned on in the Preferences in the Wrangler View UI. Job Tags are explained in detail on the Job Tags page.
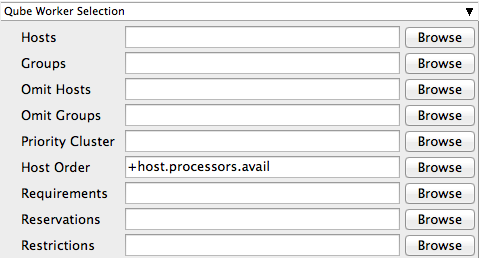
Hosts
Explicit list of Worker hostnames that will be allowed to run the job (comma-separated).
Groups
Explicit list of Worker groups that will be allowed to run the job (comma-separated). Groups identify machines through some attribute they have, eg, a GPU, an amount of memory, a license to run a particular application, etc. Jobs cannot migrate from one group to another. See worker_groups.
Omit Hosts
Explicit list of Worker hostnames that are not allowed run the job (comma-separated).
Omit Groups
Explicit list of Worker groups that are not allowed to run the job (comma-separated).
Priority Cluster
Clusters are non-overlapping sets of machines. Your job will run at the given priority in the given cluster. If that cluster is full, the job can run in a different cluster, but at lower priority. Clustering
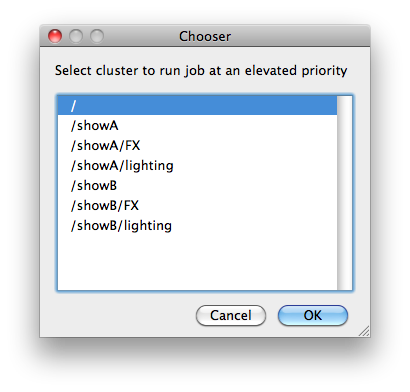 |
|---|
Example:
|
Host Order
Order to select Workers for running the job (comma-separated) [+ means ascending, - means descending].
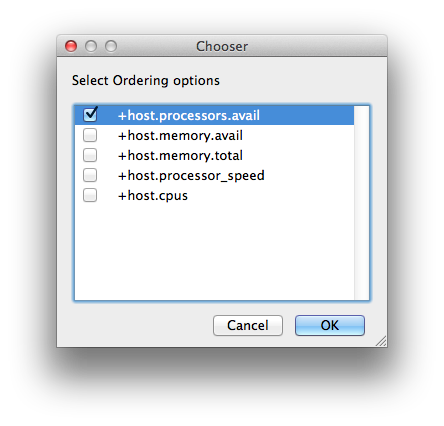 |
|---|
Host Order is a way of telling the job how to select/order workers
|
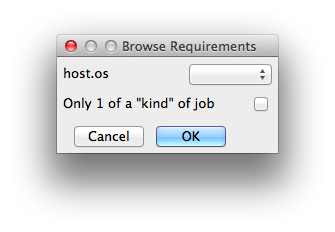
Requirements
Worker properties needed to be met for job to run on that Worker (comma-separated, expression-based). Click 'Browse' to choose from a list of Host Order Options.
 |
|---|
Requirements is a way to tell the workers that this job needs specific properties to be present in order to run. The drop-down menu allows a choice of OS:
You can also add any other Worker properties via plain text. Some examples:
With integer values, you can use any numerical relationships, e.g. =, <, >, <=, >=. This won't work for string values or floating point values. Multiple requirements can also be combined with AND and OR (the symbols && and || will also work). The 'Only 1 of a "kind" of job' checkbox will restrict a Worker to running only one instance with a matching "kind" field (see below). The prime example is After Effects, which will only allow a single instance of AE on a machine. Using this checkbox and the "Kind" field, you can restrict a Worker to only one running copy of After Effects, while still leaving the Worker's other slots available for other "kinds" of jobs. |
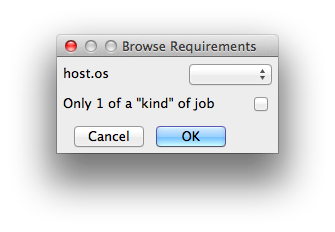
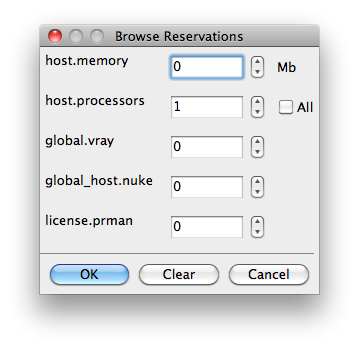
Reservations
Worker resources to reserve when running job (comma-separated, expression-based).
  |
|---|
Reservations is a way to tell the workers that this job will reserve the specific resources for this job. Menu items:
Other options:
|
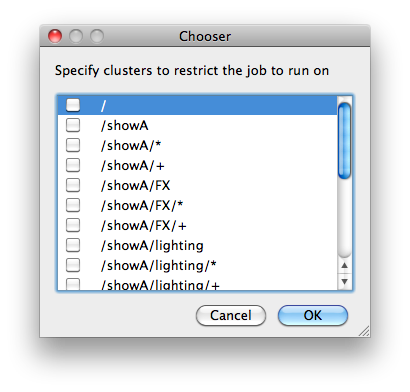
Restrictions
Restrict job to run only on specified clusters ("||"-separated) [+ means all below, * means at that level]. Click 'Browse' to choose from a list of Restrictions Options.
 |
|---|
Restrictions is a way to tell the workers that this job can only run on specific clusters. You can choose more than one cluster in the list. Examples:
|
See Also
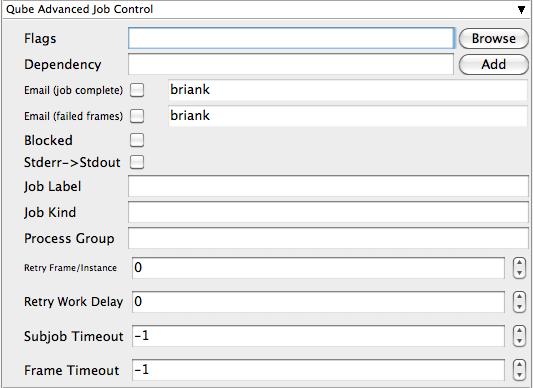
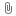
Flags
List of submission flag strings (comma separated). Click 'Browse' to choose required job flags.
|
|---|
| See this page for a full explanation of flag meanings |
Dependency
Wait for specified jobs to complete before starting this job (comma-separated). Click 'Add' to create dependent jobs.
 |
|---|
You can link jobs to each other in several ways:
The second menu chooses between "job" (the entire set of frames) and "work" (typically a frame). So to link frame 1 of one job to frame 1 of a second, job, you would choose "work" in this menu. If you want to wait for all the frames of one job to complete before starting a second, then choose "job". The other option, "subjob", refers to the instance of a job. This is much less common, but means that, for example, the instance of Maya that was running frames has completed. For a complete description on how to define complex dependencies between jobs or frames, please refer to the Callbacks section of the Developers Guide. |
Email (job complete)
Send email on job completion (success or failure). Sends mail to the designated user.
Email (failed frames)
Sends mail to the designated user if frames fail.
Blocked
Set initial state of job to "blocked".
Stderr->Stdout
Redirect and consolidate the job stderr stream to the stdout stream. Enable this if you would like to combine your logs into one stream.
Job Label
Optional label to identify the job. Must be unique within a Job Process Group. This is most useful for submitting sets of dependent jobs, where you don't know in advance the job IDs to depend on, but you do know the labels.
Job Kind
Arbitrary typing information that can be used to identify the job. It is commonly used to make sure only one of this "kind" of job runs on a worker at the same time by setting the job's requirements to include "not (job.kind in host.duty.kind)". See How to restrict a host to only one instance of a given kind of job, but still allow other jobs
Process Group
Job Process Group for logically organizing dependent jobs. Defaults to the jobid. Combination of "label" and "Process Group" must be unique for a job. See Process group labels
Retry Frame/Instance
Number of times to retry a failed frame/job instance. The default value of -1 means don't retry.
Retry Work Delay
Number of seconds between retries.
Subjob Timeout
Kill the subjob process if running for the specified time (in seconds). Value of -1 means disabled. Use this if the acceptable instance/subjob spawn time is known.
Frame Timeout
Kill the agenda/frame if running for the specified time (in seconds). Value of -1 means disabled. Use this if you know how long frames should take, so that you can automatically kill those running long.
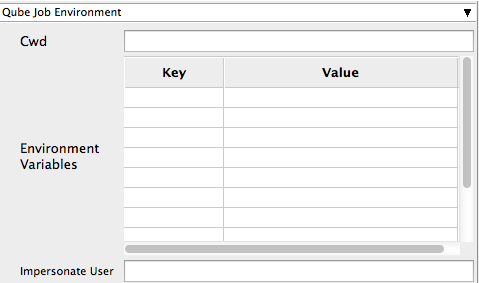
Cwd
Current Working Directory to use when running the job.
Environment Variables
Environment variables override when running a job. You can specify key/value pairs of environment variables
This is useful when you might need different settings for your render applications based on different departments or projects.
Impersonate User
You can specify which user you would like to submit the job as. The default is the current user. The format is simply <username>. This is useful for troubleshooting a job that may fail if sent from a specific user.
Example:
Setting "josh" would attempt to submit the job as the user "josh" regardless of your current user ID.
Note: In order to do this, the submitting user must have "impersonate user" permissions.
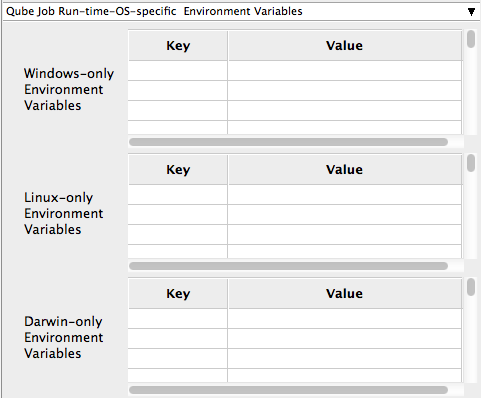
Windows-only Environment Variables
Used to provide OS specific environment variables for Windows. Enter variables and values to override when running jobs.
Linux-only Environment Variables
Used to provide OS specific environment variables for Linux. Enter variables and values to override when running jobs.
Darwin-only Environment Variables
Used to provide OS specific environment variables for OS X. Enter variables and values to override when running jobs.
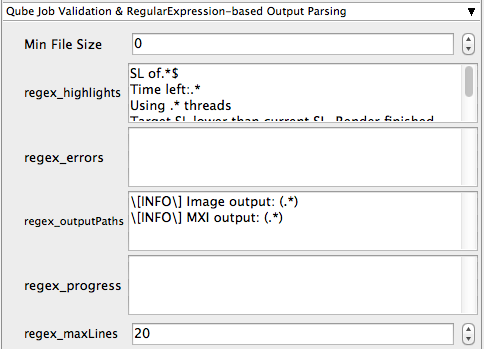
Min File Size
Used to test the created output file to ensure that it is at least the minimum size specified. Put in the minimum size for output files, in bytes. A zero (0) disables the test.regex_highlights
Used to add highlights into logs. Enter a regular expression that, if matched, will be highlighted in the information messages from stdout/stderr.
regex_errors
Used to catch errors that show up in stdout/stderr. For example, if you list "error: 2145" here and this string is present in the logs, the job will be marked as failed. This field comes pre-populated with expressions based on the application you are submitting from. You can add more to the list, one entry per line.
regex_outputPaths
Regular expression for identifying outputPaths of images from stdout/stder. This is useful for returning information to the Qube GUI so that the "Browse Ouput" right-mouse menu works.
regex_progress
Regular expression for identifying in-frame/chunk progress from stdout/stderr. Used to identify strings for relaying the progress of frames.
regex_maxlines
Maximum number of lines to store for regex matched patterns for stdout/stderr. Used to truncate the size of log files.
GenerateMovie
Select this option to create a secondary job that will wait for the render to complete then combine the output files into a movie.
Note: For this to work correctly the "Qube (ImagesToMovie) Job..." has to be setup to use your studios transcoding application.
Account
Arbitrary accounting or project data (user-specified). This can be used for creating tags for your job.
You can add entries by typing in the drop-down window or select already created accounts from the drop-down.
See also Qube! Job Tags
Notes
Freeform text for making notes on this job. Add text about the job for future reference. Viewable in the Qube UI.
- No labels
- Powered by Scroll Content Management Add-ons for Atlassian Confluence 5.6.6 | 2.8.10
- Powered by Scroll Content Management Add-ons for Atlassian Confluence.